

The first historical records of Château Plain Point date back to the year 1480. Embark on a journey through several centuries of history.
In 2023, Château Plain Point entered a new era with the construction of a custom-designed winery to showcase the terroir.
It is the alchemy between its landscapes, its mosaic of soils, its oceanic climate, and its location at the confluence of two major rivers that creates the unique soul of Château Plain Point wines.
At Château Plain Point, we work like the greatest artisans to delicately and precisely reveal the nuances and subtleties of our terroir.

"The harmony of contrasts"
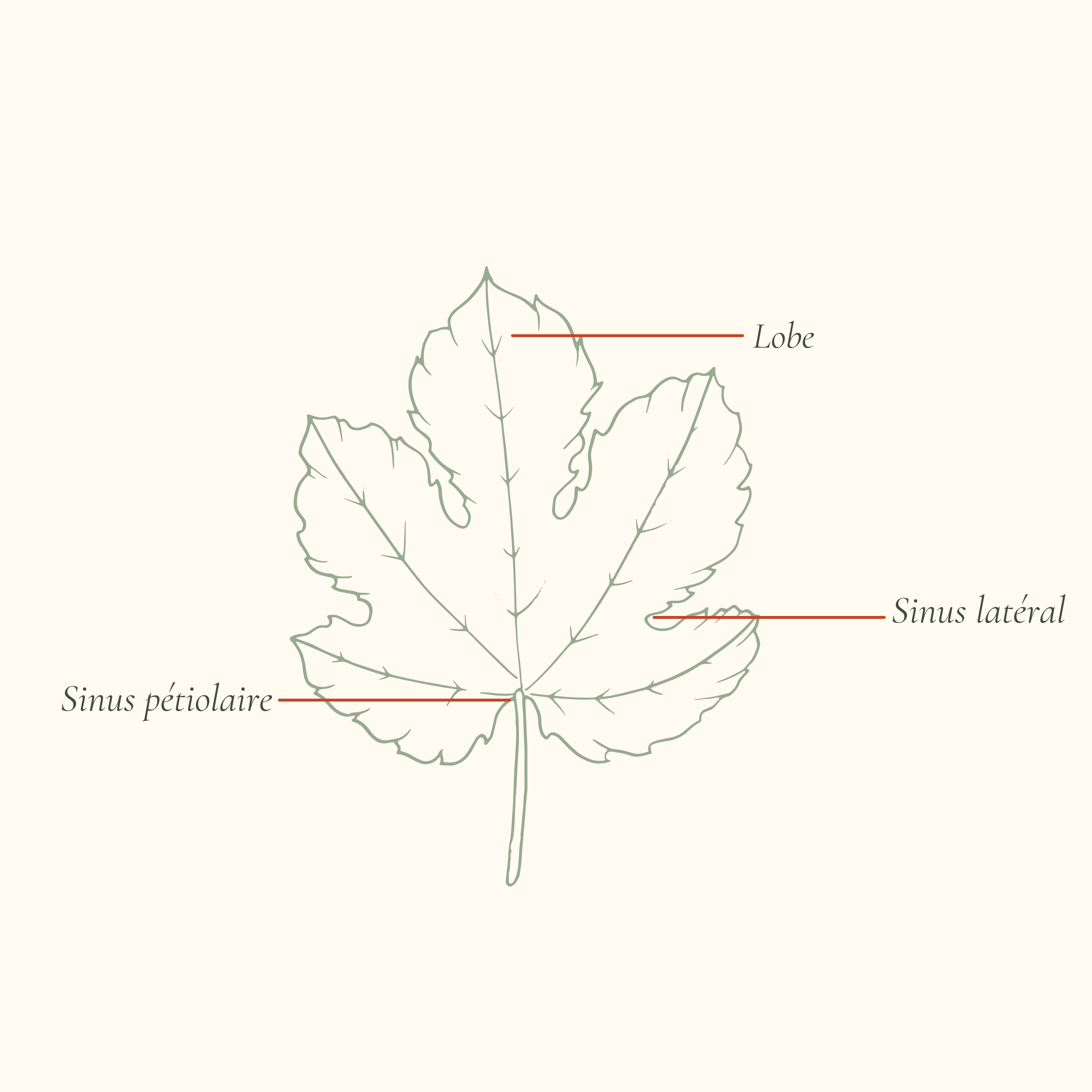
Our grape varieties have been chosen according to our terroir. Each has its own identity and can be easily recognized with the naked eye thanks to a study called ampelography.

This grape variety originates from the Bordeaux vineyard. According to genetic analyses, Merlot is believed to be a cross between Cabernet Franc and Magdeleine Noire des Charentes.
How to recognize it:
Wedge-shaped form
Five or seven lobes
Open petiolar sinus
U-shaped base, sometimes with the bottom limited by the vein near the petiolar point
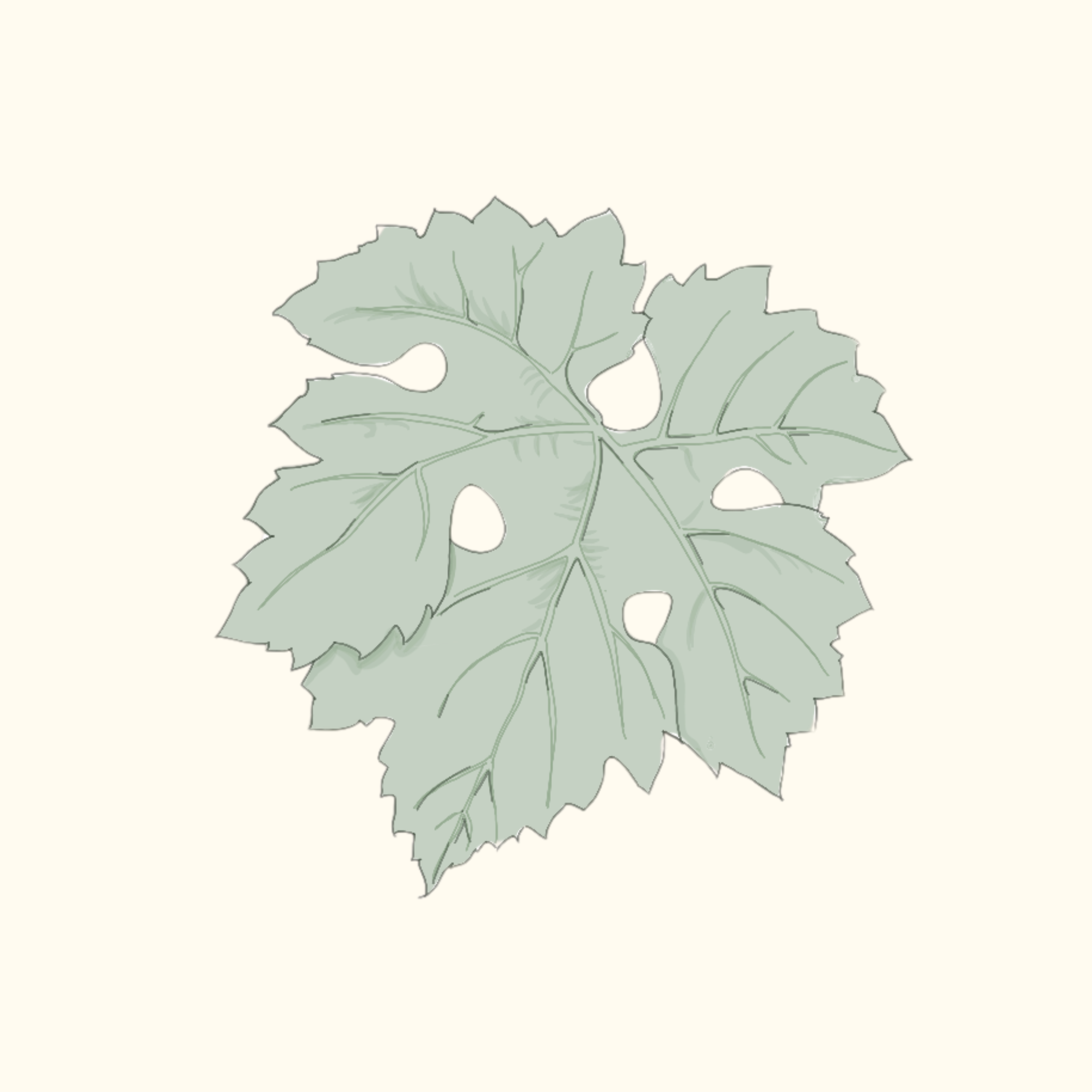
This grape variety, originating from the Bordeaux region, is believed—according to published genetic analyses—to be a cross between Cabernet Franc and Sauvignon.
How to recognize it:
Deep petiolar sinus in a wide and very rounded U-shape
Slightly overlapping lobes
Orbicular (round) shape
Seven lobes

Cabernet Franc is one of the oldest grape varieties in Bordeaux and the parent of three other red grape varieties in the Bordeaux vineyard: Cabernet Sauvignon, Merlot, and Carmenère.
How to recognize it:
Pentagon-shaped form
Five or seven lobes
Petiolar sinus shaped like a lyre
U-shaped base, sometimes with the bottom limited by the vein near the petiolar point
Teeth at the base of the petiole

Central France or the Southwest are the two possible origin zones for this grape variety. According to published genetic analyses, Sauvignon is directly related to Savagnin. Sauvignon is sometimes called 'Savagnou' in the Pyrénées-Atlantiques, 'Douce blanche,' 'Blanc doux,' or 'Libournais' in Dordogne.
How to recognize it:
Petiolar sinus slightly open to open
Medium-sized teeth
Orbicular (round) shape
Five lobes
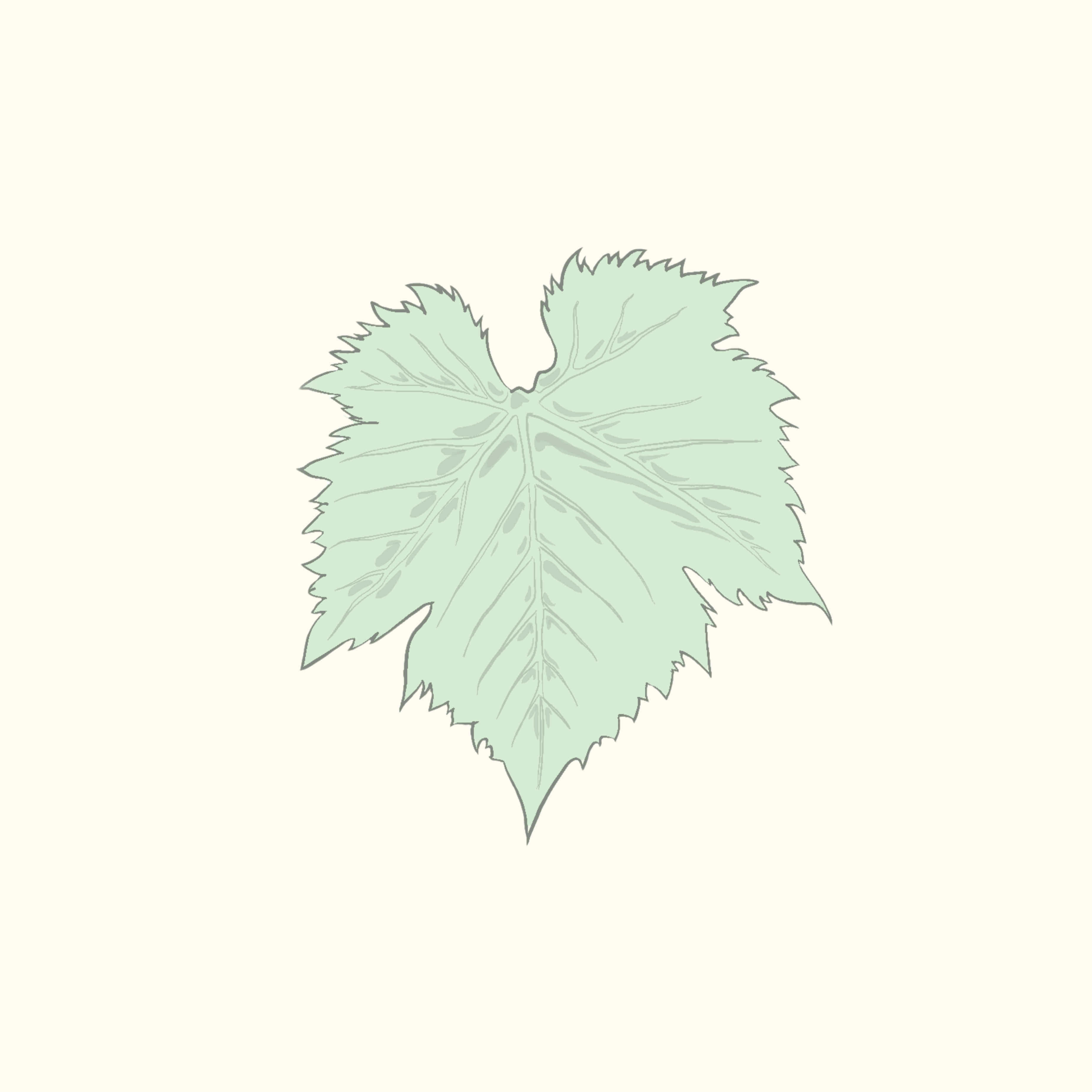
It is believed to have appeared in the 16th century, resilient and hardy, aromatic, and often very high in sugar concentration. After the phylloxera crisis, it largely replaced Sauvignon Blanc in the Southwest of France, representing 80% of the grape plantings in Aquitaine at the beginning of the 20th century.
How to recognize it:
Orbicular (round) shape
Five lobes
Petiolar sinus more or less open
Highly serrated
